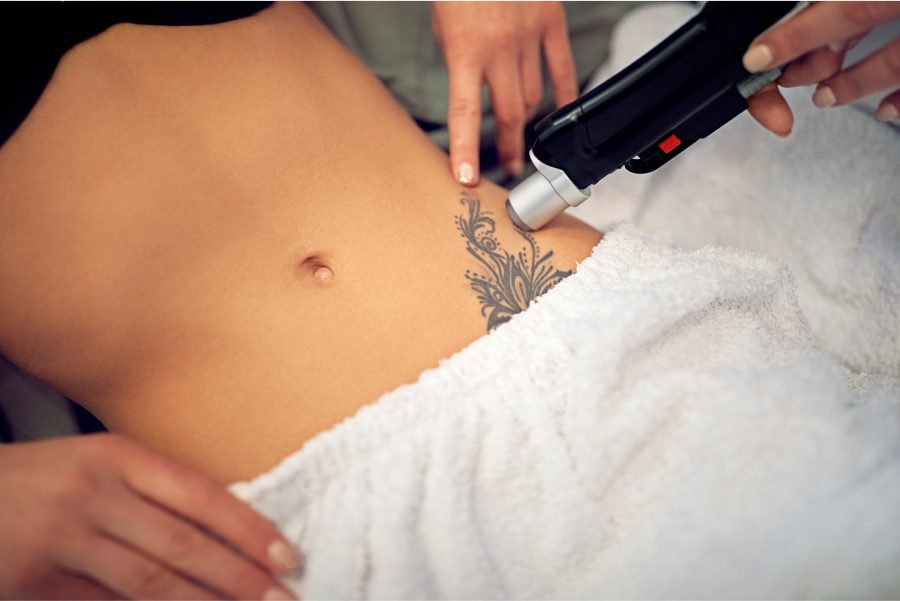
Laser tattoo removal uses focused light energy to break down tattoo pigments, allowing the body’s immune system to gradually eliminate them. Q-switched and picosecond lasers are most commonly used, with treatment selection based on tattoo colors, size, age, and skin type. Multiple sessions are typically required for complete removal, though significant fading is often achievable.
During treatment, laser pulses target tattoo pigments while minimizing damage to surrounding skin. Sessions last 15-30 minutes depending on tattoo size, with treatments spaced 6-8 weeks apart to allow proper healing. Topical anesthesia or cooling devices help manage discomfort during the procedure.
Common side effects include immediate swelling, redness, and possible blistering at the treatment site. Temporary changes in skin pigmentation may occur, with darker skin tones at higher risk for permanent discoloration. Scarring is possible but uncommon when proper aftercare is followed. Some patients experience temporary textural changes in the treated area.
Visible fading typically begins after 4-6 weeks following the first treatment. Significant improvement usually requires 6-12 sessions or more, depending on tattoo characteristics. Amateur tattoos generally respond better than professional ones, and darker colors like black and red fade more readily than lighter colors. Complete removal may take 12-24 months, though many patients achieve satisfactory fading earlier in the process.
Learn More About Medical Weight Loss
Medical weight loss programs combine physician to practitioner supervision with personalized treatment plans to achieve sustainable weight reduction. These programs may include prescription medications, nutritional counseling, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes...